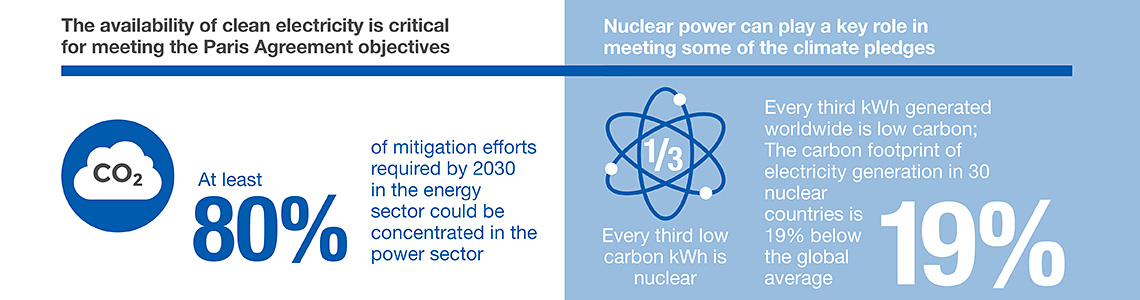
With the adoption of the Paris Agreement in 2015, almost all Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) agreed to prepare nationally determined contributions (NDCs) to control GHG emissions and limit the increase of global mean surface temperature by the end of the century to below 2°C relative to pre-industrial levels. Since then, increasing scientific understanding of the significant risks associated with warming of 2°C, along with increasing societal concern, have established the need for more urgent and ambitious action to avoid the worst impacts of climate change, by limiting warming to 1.5°C.